Starting from December 2019, a new course on additive manufacturing technologies is given to students majoring in Modeling and Numerical Mechanics and Industry 4.0. The course provides theoretical and practical opportunities for engineering students to practise a key technology for the industry of the future.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is the process of creating an object by building one layer at a time and allows building 3D objects by adding layer-upon-layer of material from computer-aided design (CAD) models.
A key process in perpetual evolution
This new manufacturing process contrasts with traditional subtractive manufacturing technologies, in which materials are shaped by material removal. Additive manufacturing finds application in several areas such as medical, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, military, daily consumption.
Among the fields relying on additive manufacturing are:
-
- Preproduction rapid prototyping
- The machine tool industry
- Product customization or personalization
- Small series production
Other sectors, such as bioprinting, food industry or architecture, are currently under development, but become progressively more popular.
All in all, research firm Gartner expects that by 2023, 25 per cent of medical devices produced within developed markets will be printed in 3D. The technology will facilitate delicate surgical procedures and will allow new applications—from implants and surgical tools to tissues and functioning organs.
ESILV partners with Ansys and Lynxter to provide cutting-edge theoretical and practical approaches
The new course is given by Jacques Duysens, Business Development Director EMEA at ANSYS and ESILV Advisor in Industrial Strategy and International Relations.
This expert in automotive engineering is also in charge of the courses that is related to Digital Twin. That’s another innovative module offered to ESILV’s students majoring in Digital Mechanics and Modeling and Industry 4.0.
In the 5th year, students will explore the following themes :
- Additive Manufacturing Technology Issues
- General introduction to various Modeling & Simulation techniques
- The extrusion-based Additive Manufacturing (EAM) technique
- The notion of function-based design
In order to move from theory to practice, the engineering students use a state-of-the-art machine provided by Bayonne-based French startup Lynxter.
#Formation
L'@ESilv lance un nouveau cours « Fabrication Additive » avec @Lynxter_3D et @ANSYS. Présentation ! #impression3d #fabricationadditive #ESILV #CESI https://t.co/5WxaCzUND7— A3DM Magazine (@A3DM_Magazine) December 19, 2019
This modular and open tool, which is added to ESILV’s fleet of 3D printers, allows students to choose an adapted configuration by simply changing the tool head of the machine.
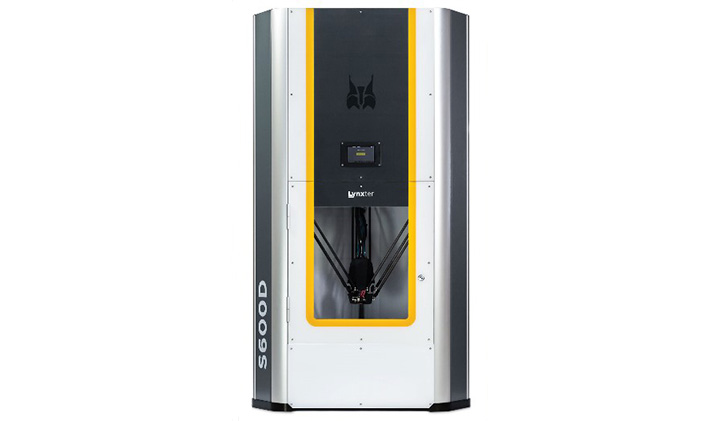

LYNXTER S600D machine acquired by ESILV for research and training purposes
Thus, the multi-material and multiprocess printing programmes allow ESILV students to use thermoplastic filaments, liquids (silicons, inks…), pastes (ceramics) and to explore various applications in make-to-order production, small series, and the development of new processes.
This new educational tool is led by Lynxter, which brings its experience in additive manufacturing, and ANSYS Inc. through its “Ansys AM Simulation Tools” software suite. The process addresses the complete additive manufacturing workflow including topology optimization, validation, printing process through to material development
Find out more about the Modelling and Numerical Mechanics and Industry 4.0 courses available within the engineering curriculum at ESILV (The Leonard de Vinci Engineering School ).